1. Enable quantum-safe network transport with ANYsec#
| Activity name | Enable quantum-safe network transport with ANYsec |
| Activity ID | 41 |
| Short Description | ANYsec is a scalable, flexible and quantum-safe Nokia technology that delivers low-latency, line-rate native encryption across any transport (IP, MPLS, Segment Routing, Ethernet, or VLAN) on any service, at any time, and under any load conditions, all without impacting performance. |
| Difficulty | Beginner |
| Tools used | SROS MD-CLI, EdgeShark, Wireshark, TShark, gNMIc, pySROS |
| Topology Nodes | PE1, PE2, Client01, Client02 |
| References | ANYsec Guide ANYsec/MACsec Demo ANYsec Demo IP Network Security Nokia FP5 security ANYsec application note MD-CLI explorer tool pySROS documentation |
ANYsec: Scalable, High-Performance Network Encryption by Nokia
ANYsec is Nokia’s cutting-edge network encryption solution, introduced with FP5 silicon and available from SR OS 23.10.R1. Designed for today’s and tomorrow’s security needs, ANYsec delivers low-latency, line-rate encryption that’s scalable, flexible, and quantum-safe.
Building on MACsec standards, ANYsec extends encryption beyond traditional Layer 2 boundaries, offering native, service-agnostic encryption at Layers 2, 2.5, and 3. It supports IP, MPLS, Segment Routing, Ethernet, and VLAN transports, securing any service under any load without impacting network performance.
With its simple deployment model and powerful architecture, ANYsec brings robust encryption to modern service provider and enterprise networks without compromise.
1.1 Objective#
In a multivendor IP/MPLS network where your customers are requesting you to provide quantum-safe transport encryption for their existing services, Nokia FP5-based PE nodes with ANYsec can truly be your magic bullet.
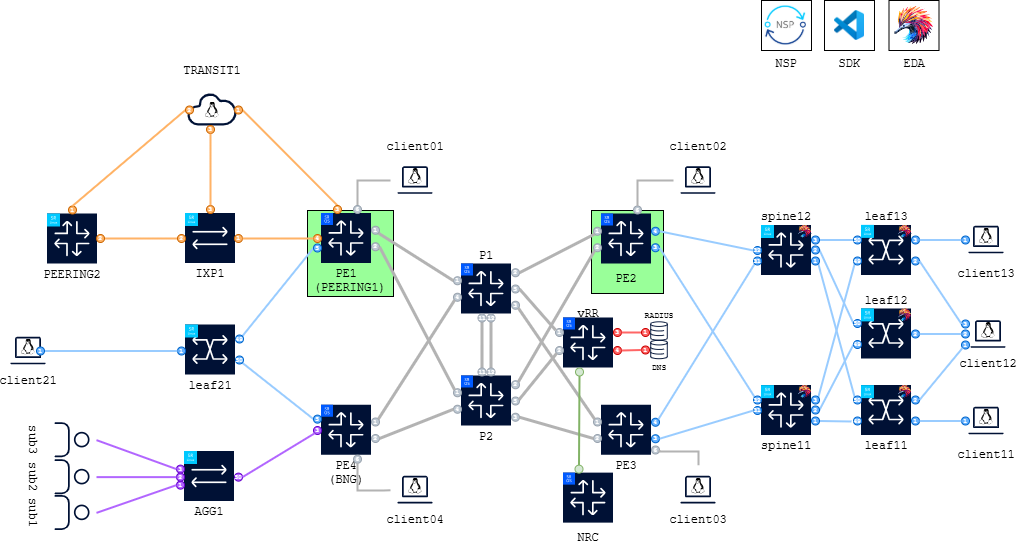
For this activity we will use the PE1 and PE2 FP5-based routers to configure an IP/MPLS service with ANYsec transport between client01 and client02. The Fig. 1. below highlights the FP5 PEs that will be used in this activity:
In this activity you will:
- Enable the network to support ANYsec and create a simple MPLS service to interconnect two client hosts.
- Configure the client hosts, test the connectivity and use Wireshark, Edgeshark or TCPDump to observe the ANYsec packet headers.
- Create gNMIc scripts to create new ANYsec enabled services, enable or disable ANYsec for a service to demonstrate how easy is to automate ANYsec activation. You'll also create a network failure to observe that ANYsec, as any other MPLS packets, are not impacted.
- Finally we challenge you to automate ANYsec services using other technologies e.g with Python and pySROS.
1.2 Technology explanation#
ANYSec is a Nokia network encryption solution available with the new FP5 models introduced in the SR OS 23.10.R1 release. It is a low-latency line-rate encryption mechanism that is scalable, flexible and quantum-safe. Based on MACSec standards as the foundation, ANYsec has flexibility to offset the authentication and encryption to allow L2, L2.5 and L3 encryption. It is currently supported for SR-ISIS, SR-OSPF and SR-OSPFv3. ANYsec encapsulates MKA over IP/UDP and supports tunnel slicing using Flex Algo or multi-instance IGP.
1.3 Lab topology overview#
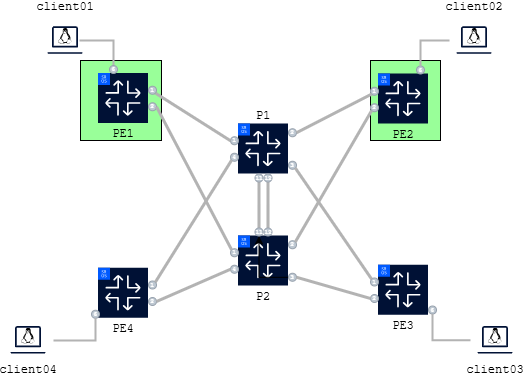
For this activity we will focus on a subset of the main topology considering only the SROS PEs, the P routers and clients. The PE1 and PE2 nodes are FP5-based and will be configured with ANYsec and IP/MPLS services to provide quantum-safe transport between client01 and client02, as illustrated in Fig. 2. below:
The network is already configured with IGP, MPLS, BGP and several existing services. In the following tasks we will add additional configuration to enable ANYsec in the network for new or existing services.
1.4 Tasks#
You should read these tasks from top-to-bottom before beginning the activity.
It is tempting to skip ahead but tasks may require you to have completed previous tasks before tackling them.
1.4.1 Configuring the network for ANYsec#
Generally, the steps required for enabling ANYsec in the network are the following:
- Configure MACsec connectivity-association (CA).
ANYsec uses MACsec encryption engine and MACsec Key Agreement protocol (MKA – part of 802.1X extensions) - Add ANYsec-specific configuration:
- Choose a UDP port for MKA
- Select MPLS labels to reserve and use
- Add a security termination policy that lets the router decide which LSPs it should decrypt
- List the peers that use the same CA and pre-shared key (PSK) to exchange datapath security association keys (SAKs) in an encryption-group
- Configure SDPs that use
sr-isis - Configure the services to use those SDPs for ANYsec
You should use the ANYsec guide for more details and guidance with the following tasks.
1.4.1.1 Configure CA#
Your first task is to configure a connectivity-association at both PE1 and PE2. Follow the ANYsec guide and use the following parameters:
- CA name: "CA_VLL-1001"
- cipher-suite: gcm-aes-xpn-128
- PSK encryption-type: aes-128-cmac
- PSK cak: 0123456789ABCDEF0123456789ABCDEF
Hint
This is a template to configure a MACsec CA:
/edit global
/configure {
macsec {
connectivity-association <CA name> {
admin-state enable
cipher-suite <cipher>
anysec true
static-cak {
mka-hello-interval 5
pre-shared-key 1 {
encryption-type <enc-type>
cak <cak>
cak-name <cak-name>
}
pre-shared-key 2 {
encryption-type <enc-type>
cak <cak>
cak-name <cak-name>
}
}
}
}
}
commit
Solution
This is the configuration:
/edit global
/configure {
macsec {
connectivity-association "CA_VLL-1001" {
admin-state enable
cipher-suite gcm-aes-xpn-128
anysec true
static-cak {
mka-hello-interval 5
pre-shared-key 1 {
encryption-type aes-128-cmac
cak "0123456789ABCDEF0123456789ABCDEF"
cak-name "0123456789ABCDEF0123456789ABCDEF" # for tests only we use the name equal to the cak
}
pre-shared-key 2 {
encryption-type aes-128-cmac
cak "123456789ABCDEF0123456789ABCDEF0"
cak-name "123456789ABCDEF0123456789ABCDEF0" # for tests only we use the name equal to the cak
}
}
}
}
}
commit
After configuring both PEs, validate the MACsec CA configuration.
[/]
A:admin@g15-pe1# show macsec connectivity-association "CA_VLL-1001" detail
===============================================================================
Connectivity Association "CA_VLL-1001"
===============================================================================
Admin State : Up
Description : (Not Specified)
Delay Protection : Disabled
Replay Protection : Disabled
Replay Window Size : 0
Macsec Encrypt : Enabled
Clear Tag Mode : none
Cipher Suite : gcm-aes-xpn-128
Encryption Offset : 0
Assigned ports : None
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Static Cak
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MKA Key Server Priority : 16
Active Pre-Shared-Key Index : 1
Hello Interval : 5
Active Pre-Shared-Key CKN : 0123456789ABCDEF0123456789ABCDEF
Encryption Type : aes-128-cmac
===============================================================================
[/]
A:admin@g15-pe1#
1.4.1.2 Configure ANYsec#
In this next task, ANYsec itself will be added to the configuration. Use the following parameters:
- mka-udp-port: 10000
- mpls-labels reserved-label-block:
- name=Anysec
- start=32000
- end=35999
- security-termination-policies
- name STP_VLL-1001
- local-address 10.46.${INSTANCE_ID}.{ 21, 22 } # depending on the node; {PE1, PE2}
- protocol sr-isis
- igp-instance-id 0
- tunnel-encryption encryption-group
- name "EG_VLL-1001"
- security-termination-policy STP_VLL-1001
- encryption-label { 32101, 32102} # depending on the node; {PE1, PE2}
- ca-name CA_VLL-1001
- peer-tunnel-attributes
- protocol sr-isis
- igp-instance-id 0
- peer 10.46.${INSTANCE_ID}.{ 22, 21 } # depending on the node; {PE1, PE2}
Note
Replace ${INSTANCE_ID} with your Group ID.
As suggested before, you may use the ANYsec guide and dig in the CLI.
Hint
This is a template to configure ANYsec:
/edit global
/configure {
router "Base" {
mpls-labels {
reserved-label-block <RLB name> {
start-label <start>
end-label <end>
}
}
}
anysec {
reserved-label-block <RLB name>
mka-over-ip {
mka-udp-port <port>
}
security-termination-policies {
policy <STP name> {
admin-state enable
local-address <IP>
rx-must-be-encrypted false
protocol <protocol>
igp-instance-id <id>
}
}
tunnel-encryption {
encryption-group <TE name> {
admin-state enable
security-termination-policy <STP name>
encryption-label <enc label>
ca-name <CA name>
peer-tunnel-attributes {
protocol <protocol>
igp-instance-id <id>
}
peer <peer IP> {
admin-state enable
}
}
}
}
}
commit
Solution
/edit global
/configure {
router "Base" {
mpls-labels {
reserved-label-block "Anysec" {
start-label 32000
end-label 35999
}
}
}
anysec {
reserved-label-block "Anysec"
mka-over-ip {
mka-udp-port 10000
}
security-termination-policies {
policy "STP_VLL-1001" {
admin-state enable
local-address 10.46.${INSTANCE_ID}.21 ### Replace ${INSTANCE_ID} with your Group ID
rx-must-be-encrypted false
protocol sr-isis
igp-instance-id 0
}
}
tunnel-encryption {
encryption-group "EG_VLL-1001" {
admin-state enable
security-termination-policy "STP_VLL-1001"
encryption-label 32101
ca-name "CA_VLL-1001"
peer-tunnel-attributes {
protocol sr-isis
igp-instance-id 0
}
peer 10.46.${INSTANCE_ID}.22 { ### Replace ${INSTANCE_ID} with your Group ID
admin-state enable
}
}
}
}
}
compare
commit
#
/edit global
/configure {
router "Base" {
mpls-labels {
reserved-label-block "Anysec" {
start-label 32000
end-label 35999
}
}
}
anysec {
reserved-label-block "Anysec"
mka-over-ip {
mka-udp-port 10000
}
security-termination-policies {
policy "STP_VLL-1001" {
admin-state enable
local-address 10.46.${INSTANCE_ID}.22
rx-must-be-encrypted false
protocol sr-isis
igp-instance-id 0
}
}
tunnel-encryption {
encryption-group "EG_VLL-1001" {
admin-state enable
security-termination-policy "STP_VLL-1001"
encryption-label 32102
ca-name "CA_VLL-1001"
peer-tunnel-attributes {
protocol sr-isis
igp-instance-id 0
}
peer 10.46.${INSTANCE_ID}.21 {
admin-state enable
}
}
}
}
}
compare
commit
#
After configuring both PEs, validate the ANYsec configurations.
(gl)[/]
A:admin@g15-pe1# /show router mpls-labels label-range
===============================================================================
Label Ranges
===============================================================================
Label Type Start Label End Label Aging Available Total
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Static 32 18431 - 18400 18400
Dynamic 18432 524287 0 492848 505856
Seg-Route 21000 30000 - 0 9001
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Reserved Label Blocks
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Reserved Label Start End Total
Block Name Label Label
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Anysec 32000 35999 4000
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
No. of Reserved Label Blocks: 1
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
===============================================================================
(gl)[/]
A:admin@g15-pe1#
(gl)[/]
A:admin@g15-pe1# show anysec mka-over-ip
===============================================================================
MKA over IP
===============================================================================
MKA over IP session UDP Port: 10000
Reserved Label Block : Anysec
Operational Status : in-service
===============================================================================
(gl)[/]
A:admin@g15-pe1#
(gl)[/]
A:admin@g15-pe1# /show anysec tunnel-encryption detail
===============================================================================
Encryption Group: EG_VLL-1001
===============================================================================
Group Admin State : Up
CA Name : CA_VLL-1001
Local Encryption Label : 32101
Security Termination Policy: STP_VLL-1001
Policy Admin State : Up
Policy Protocol : sr-isis
Policy IGP Instance ID : 0
Policy FlexAlgo ID : 0
Local Address : 10.46.15.21
Rx Must Be Encrypted : No
Terminating Label : 21021
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Peer 10.46.15.22 configuration
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Peer Admin State : Up
Peer Protocol : sr-isis
Peer IGP Instance ID : 0
Peer FlexAlgo ID : 0
Peer Tunnel ID : 524297
Peer Encryption Label : 32102
Last Inconsistent Rx SCI: 0000000000000000
Peer Oper State : Up
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SC stats for peer 10.46.15.22
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
txSCSecyStats
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Tx SCI : 000000007d650001
Encrypted Packets : 0
Encrypted Octets : 0
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
rxSCSecyStats
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Rx SCI : 000000007d660001
Delay Packets : 0
Not Valid Packets : 0
Unchecked Packets : 0
OK Packets : 0
Decrypted Octets : 0
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
===============================================================================
(gl)[/]
A:admin@g15-pe1#
1.4.1.3 Configure SDP#
Your next task is to configure an SDP to provide connectivity between both PE1 and PE2. This SDP will use ANYsec to encrypt the VLL service data. Use the following parameters respectively:
- PE1
- SDP-ID: 1222
- sr-isis
- far-end IP: 10.46.${INSTANCE_ID}.22 ### Replace ${INSTANCE_ID} with your Group ID
- PE2
- SDP-ID: 1111
- sr-isis
- far-end IP: 10.46.${INSTANCE_ID}.21 ### Replace ${INSTANCE_ID} with your Group ID
Hint
This is the SDP template:
Solution
These are the SDP configurations for both PEs.
After configuring both PEs, validate that the SDP are up at both PEs.
[/]
A:admin@g15-pe1# show service sdp
============================================================================
Services: Service Destination Points
============================================================================
SdpId AdmMTU OprMTU Far End Adm Opr Del LSP Sig
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
1222 0 8642 10.46.15.22 Up Up MPLS I TLDP
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Number of SDPs : 1
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Legend: R = RSVP, L = LDP, B = BGP, M = MPLS-TP, n/a = Not Applicable
I = SR-ISIS, O = SR-OSPF, T = SR-TE, F = FPE
============================================================================
[/]
A:admin@g15-pe1#
[/]
A:admin@g15-pe1# show service sdp detail
===============================================================================
Services: Service Destination Points Details
===============================================================================
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Sdp Id 1222 -10.46.15.22
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Description : To PE2 - Epipe using ISIS 0
SDP Id : 1222 SDP Source : manual
Admin Path MTU : 0 Oper Path MTU : 8642
Delivery : MPLS
Far End : 10.46.15.22 Tunnel Far End : n/a
Oper Tunnel Far End : 10.46.15.22
LSP Types : SR-ISIS
Admin State : Up Oper State : Up
Signaling : TLDP Metric : 0
Acct. Pol : None Collect Stats : Disabled
Last Status Change : 05/03/2025 07:50:41 Adv. MTU Over. : No
Last Mgmt Change : 05/03/2025 01:32:20 VLAN VC Etype : 0x8100
Bw BookingFactor : 100 PBB Etype : 0x88e7
Oper Max BW(Kbps) : 0 Avail BW(Kbps) : 0
Net-Domain : default Egr Interfaces : Consistent
FPE LSP Id : 0
Weighted ECMP : Disabled
Flags : None
Mixed LSP Mode Information :
Mixed LSP Mode : Disabled Active LSP Type : SR-ISIS
KeepAlive Information :
Admin State : Disabled Oper State : Disabled
Hello Time : 10 Hello Msg Len : 0
Hello Timeout : 5 Unmatched Replies : 0
Max Drop Count : 3 Hold Down Time : 10
Tx Hello Msgs : 0 Rx Hello Msgs : 0
Src B-MAC LSB : <none> Ctrl PW VC ID : <none>
Ctrl PW Active : n/a
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
RSVP/Static LSPs
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Associated LSP List :
No LSPs Associated
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Class-based forwarding :
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Class forwarding : Disabled EnforceDSTELspFc : Disabled
Default LSP : Uknwn
Multicast LSP : None
===============================================================================
FC Mapping Table
===============================================================================
FC Name LSP Name
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
No FC Mappings
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Segment Routing
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ISIS : enabled LSP Id : 524309
Oper Instance Id : 0
OSPF : disabled
TE-LSP : disabled
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Number of SDPs : 1
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
===============================================================================
[/]
A:admin@g15-pe1#
1.4.1.4 Configure VLL#
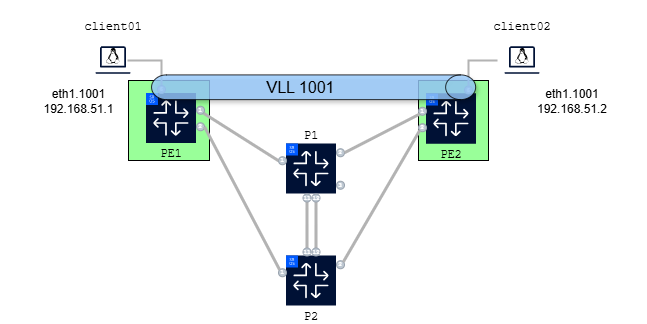
Your next task is to configure a VLL/Epipe service between PE1 and PE2 using ANYsec to interconnect client01 and client02 as shown in Fig. 3.
Use the following parameters respectively:
- service name: "anysec-vll-1001"
- service id: 1001
- spoke-sdp: 1222:1001 (on PE1) and 1111:1001 (on PE2)
- sap 1/1/c6/1:1001
If you're not familiarized with the concept of SDP (Service destination points), you may refer to the Services Overview Guide - SDP section.
Hint
This is the VLL template.
Solution
These are the VLL configurations for both PEs.
After configuring both PEs, confirm that the VLL service is active and healthy.
(gl)[/]
A:admin@g15-pe1# show service service-using epipe
===============================================================================
Services [epipe]
===============================================================================
ServiceId Type Adm Opr CustomerId Service Name
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1001 Epipe Up Up 1 anysec-vll-1001
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Matching Services : 1
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
===============================================================================
(gl)[/]
A:admin@g15-pe1#
(gl)[/]
A:admin@g15-pe1# show service id 1001 base
===============================================================================
Service Basic Information
===============================================================================
Service Id : 1001 Vpn Id : 0
Service Type : Epipe
MACSec enabled : no
Name : anysec-vll-1001
Description : Epipe using ISIS 0
Customer Id : 1 Creation Origin : manual
Last Status Change: 05/09/2025 14:12:48
Last Mgmt Change : 05/09/2025 14:12:48
Test Service : No
Admin State : Up Oper State : Up
MTU : 8100
Vc Switching : False
SAP Count : 1 SDP Bind Count : 1
Per Svc Hashing : Disabled Lbl Eth/IP L4 TEID: Disabled
Ignore MTU Mismat*: Disabled
Vxlan Src Tep Ip : N/A
Force QTag Fwd : Disabled
Lcl Switch Svc St : sap
Oper Group : <none>
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Service Access & Destination Points
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Identifier Type AdmMTU OprMTU Adm Opr
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sap:1/1/c6/1:1001 q-tag 8704 8704 Up Up
sdp:1222:1001 S(10.46.23.22) Spok 0 8678 Up Up
===============================================================================
* indicates that the corresponding row element may have been truncated.
(gl)[/]
A:admin@g15-pe1#
1.4.2 Configure clients#
Now that the network and the VLL service is configured we will configure the clients and test the connectivity. The client nodes client01 and client02 are connected to their respective PE node on interface eth1.
Configure the IP for each linux client using interface eth1:1001, vlan 1001 and subnet 192.168.51.0/24. Then verify the connectivity between the hosts.
ping -c 2 192.168.51.2
PING 192.168.51.2 (192.168.51.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.51.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=10.5 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.51.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=5.87 ms
--- 192.168.51.2 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1001ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 5.870/8.195/10.520/2.325 ms
bash#
Note
If you need to configure and test additional services you can use this procedure and add new sub-interfaces, VLANs and IP addresses.
1.4.3 Observe the traffic#
With the setup configured and tested end-to-end, the only thing missing is to inspect the ANYsec packet headers and confirm that the payload is encrypted.
The best tool for that is Edgeshark, but it requires you to install software in your laptop. If you cannot install software in your laptop, then you may use the TCPDump or Tshark instead.
Let's explore the options.
1.4.3.1 EdgeShark#
EdgeShark is installed in your VM and it exposes a Web UI on port 5001. You can access EdgeShark with the link below:
Note
You need SSH port forwarding in case you don't have direct reachability to the server. E.g.: ssh -L 5001:localhost:5001 ${INSTANCE_ID}.srexperts.net
EdgeShark allows you to visualize all containers in your server, select the interfaces you want to capture, and stream the capture to your laptop. For that you need Wireshark and install the Edgeshark external capture plugin in your laptop to allow Edgeshark to open your local Wireshark to display the packets.
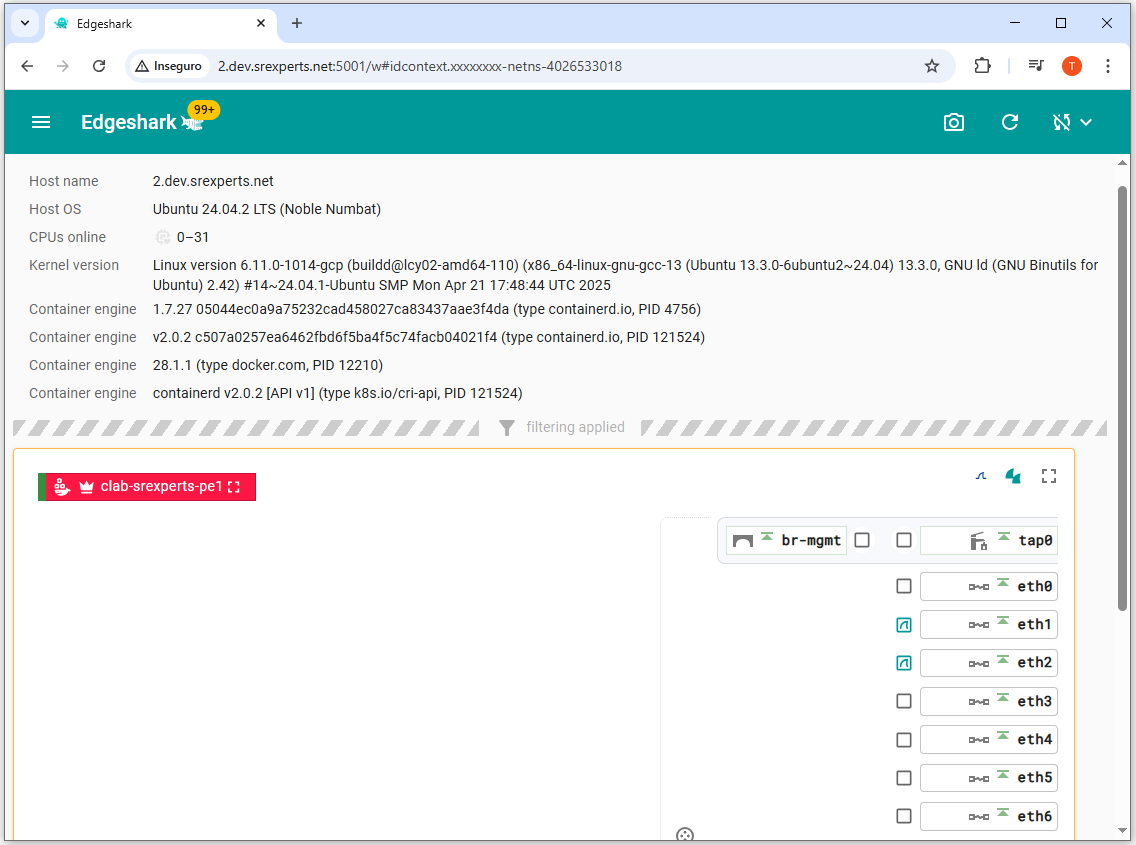
EdgeShark allows you to cature multiple interfaces simultaneously. Start a capture at PE1 eth1 and eth2 as shown below and observe the ANYsec headers.
Optionally you may consider install ANYsec Packet Dissectors for Wireshark since the public Wireshark doesn't decode the ANYsec headers. Nevertheless, you can distinguish clear text packets from ANYsec encrypted packets without these dissectors.
1.4.3.2 Tshark and Tcpdump#
One advantage of TCPdump is that it is available in most Linux systems, however it is limited in decoding protocols. You can still use it and look to the MPLS labels and verify that the 2nd label is from the ANYsec label range as shown in the output below. Tshark has more decoding capabilities and allows you to select specific interfaces to capture.
❯ sudo ip netns exec clab-srexperts-pe1 tshark -l -i eth1 -i eth2 -Y mpls -V
Capturing on 'eth1' and 'eth2'
** (tshark:2315673) 23:14:21.006908 [Main MESSAGE] -- Capture started.
** (tshark:2315673) 23:14:21.007039 [Main MESSAGE] -- File: "/tmp/wireshark_2_interfaces6QIE62.pcapng"
^Ctshark:
0 packets captured
❯ sudo ip netns exec clab-srexperts-pe1 tshark -l -i eth1 -i eth2 -Y mpls -V
Capturing on 'eth1' and 'eth2'
** (tshark:2316298) 23:14:46.597766 [Main MESSAGE] -- Capture started.
** (tshark:2316298) 23:14:46.597886 [Main MESSAGE] -- File: "/tmp/wireshark_2_interfacesNSEO62.pcapng"
Frame 3: 156 bytes on wire (1248 bits), 156 bytes captured (1248 bits) on interface eth1, id 0
Section number: 1
Interface id: 0 (eth1)
Interface name: eth1
Encapsulation type: Ethernet (1)
Arrival Time: May 11, 2025 23:14:47.383848147 EEST
[Time shift for this packet: 0.000000000 seconds]
Epoch Time: 1746994487.383848147 seconds
[Time delta from previous captured frame: 0.513804479 seconds]
[Time delta from previous displayed frame: 0.000000000 seconds]
[Time since reference or first frame: 0.517783121 seconds]
Frame Number: 3
Frame Length: 156 bytes (1248 bits)
Capture Length: 156 bytes (1248 bits)
[Frame is marked: False]
[Frame is ignored: False]
[Protocols in frame: eth:ethertype:mpls:data]
Ethernet II, Src: 0c:00:fb:9b:25:01 (0c:00:fb:9b:25:01), Dst: 0c:00:c3:81:d6:01 (0c:00:c3:81:d6:01)
Destination: 0c:00:c3:81:d6:01 (0c:00:c3:81:d6:01)
Address: 0c:00:c3:81:d6:01 (0c:00:c3:81:d6:01)
.... ..0. .... .... .... .... = LG bit: Globally unique address (factory default)
.... ...0 .... .... .... .... = IG bit: Individual address (unicast)
Source: 0c:00:fb:9b:25:01 (0c:00:fb:9b:25:01)
Address: 0c:00:fb:9b:25:01 (0c:00:fb:9b:25:01)
.... ..0. .... .... .... .... = LG bit: Globally unique address (factory default)
.... ...0 .... .... .... .... = IG bit: Individual address (unicast)
Type: MPLS label switched packet (0x8847)
MultiProtocol Label Switching Header, Label: 21021, Exp: 0, S: 0, TTL: 254
0000 0101 0010 0001 1101 .... .... .... = MPLS Label: 21021 (0x0521d)
.... .... .... .... .... 000. .... .... = MPLS Experimental Bits: 0
.... .... .... .... .... ...0 .... .... = MPLS Bottom Of Label Stack: 0
.... .... .... .... .... .... 1111 1110 = MPLS TTL: 254
MultiProtocol Label Switching Header, Label: 32102, Exp: 0, S: 1, TTL: 255
0000 0111 1101 0110 0110 .... .... .... = MPLS Label: 32102 (0x07d66)
.... .... .... .... .... 000. .... .... = MPLS Experimental Bits: 0
.... .... .... .... .... ...1 .... .... = MPLS Bottom Of Label Stack: 1
.... .... .... .... .... .... 1111 1111 = MPLS TTL: 255
Data (134 bytes)
0000 88 e5 2c 00 00 00 00 04 00 00 00 00 7d 66 00 01 ..,.........}f..
0010 41 fc d8 12 43 7a 65 b1 22 bf ee be 8e d2 d8 63 A...Cze."......c
0020 c2 a5 69 1a c4 27 1e 24 64 62 e0 e9 dd ff 9f 49 ..i..'.$db.....I
0030 50 71 70 c0 8d a3 c2 cd 52 5e 88 ea d2 96 9e 29 Pqp.....R^.....)
0040 86 13 d3 0c 39 8c cd 32 b8 d6 b8 45 77 aa 40 d0 ....9..2...Ew.@.
0050 3e 03 78 9b e7 bb 9e 17 5f d5 48 c5 d3 cf 32 11 >.x....._.H...2.
0060 bb 24 f3 76 39 d4 e1 1c 74 13 7d 89 a8 48 6b 86 .$.v9...t.}..Hk.
0070 f8 5f c4 e4 6c 04 e4 c1 73 b0 ef b2 af 88 3f cb ._..l...s.....?.
0080 26 6f c7 93 be 73 &o...s
Data: 88e52c0000000004000000007d66000141fcd812437a65b122bfeebe8ed2d863c2a5691a…
[Length: 134]
Frame 4: 156 bytes on wire (1248 bits), 156 bytes captured (1248 bits) on interface eth1, id 0
Section number: 1
Interface id: 0 (eth1)
Interface name: eth1
Encapsulation type: Ethernet (1)
Arrival Time: May 11, 2025 23:14:47.386649744 EEST
[Time shift for this packet: 0.000000000 seconds]
Epoch Time: 1746994487.386649744 seconds
[Time delta from previous captured frame: 0.002801597 seconds]
[Time delta from previous displayed frame: 0.002801597 seconds]
[Time since reference or first frame: 0.520584718 seconds]
Frame Number: 4
Frame Length: 156 bytes (1248 bits)
Capture Length: 156 bytes (1248 bits)
[Frame is marked: False]
[Frame is ignored: False]
[Protocols in frame: eth:ethertype:mpls:data]
Ethernet II, Src: 0c:00:c3:81:d6:01 (0c:00:c3:81:d6:01), Dst: 0c:00:fb:9b:25:01 (0c:00:fb:9b:25:01)
Destination: 0c:00:fb:9b:25:01 (0c:00:fb:9b:25:01)
Address: 0c:00:fb:9b:25:01 (0c:00:fb:9b:25:01)
.... ..0. .... .... .... .... = LG bit: Globally unique address (factory default)
.... ...0 .... .... .... .... = IG bit: Individual address (unicast)
Source: 0c:00:c3:81:d6:01 (0c:00:c3:81:d6:01)
Address: 0c:00:c3:81:d6:01 (0c:00:c3:81:d6:01)
.... ..0. .... .... .... .... = LG bit: Globally unique address (factory default)
.... ...0 .... .... .... .... = IG bit: Individual address (unicast)
Type: MPLS label switched packet (0x8847)
MultiProtocol Label Switching Header, Label: 21022, Exp: 0, S: 0, TTL: 255
0000 0101 0010 0001 1110 .... .... .... = MPLS Label: 21022 (0x0521e)
.... .... .... .... .... 000. .... .... = MPLS Experimental Bits: 0
.... .... .... .... .... ...0 .... .... = MPLS Bottom Of Label Stack: 0
.... .... .... .... .... .... 1111 1111 = MPLS TTL: 255
MultiProtocol Label Switching Header, Label: 32101, Exp: 0, S: 1, TTL: 255
0000 0111 1101 0110 0101 .... .... .... = MPLS Label: 32101 (0x07d65)
.... .... .... .... .... 000. .... .... = MPLS Experimental Bits: 0
.... .... .... .... .... ...1 .... .... = MPLS Bottom Of Label Stack: 1
.... .... .... .... .... .... 1111 1111 = MPLS TTL: 255
Data (134 bytes)
0000 88 e5 2c 00 00 00 00 04 00 00 00 00 7d 65 00 01 ..,.........}e..
0010 f7 60 21 f1 b6 7b c5 bf 25 d0 ae 2b fa 3a 01 54 .`!..{..%..+.:.T
0020 77 ea 45 a1 7a a4 e4 5e 39 af b3 07 92 a4 ca 93 w.E.z..^9.......
0030 be 70 63 dc bb 67 d6 d5 1c a2 bd f2 9b 58 4c 39 .pc..g.......XL9
0040 29 49 c4 84 df 98 8e 6e 49 87 8d 18 39 ab 8e 9b )I.....nI...9...
0050 ff ca 44 c8 9b 7b 76 94 20 7f 46 46 88 1b db 70 ..D..{v. .FF...p
0060 8f 4c e8 af 7d 7e 3f 9e 45 33 4d 15 e9 50 91 53 .L..}~?.E3M..P.S
0070 bf 87 6e a6 08 f1 ee 3e 10 b8 4d b3 da 38 22 8d ..n....>..M..8".
0080 32 c7 dc 3e fe 8e 2..>..
Data: 88e52c0000000004000000007d650001f76021f1b67bc5bf25d0ae2bfa3a015477ea45a1…
[Length: 134]
^Ctshark:
2 packets captured
❯
❯ sudo ip netns exec clab-srexperts-pe1 tcpdump -nni eth1 -nnvvv mpls
tcpdump: listening on eth1, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), snapshot length 262144 bytes
^C21:02:50.342036 MPLS (label 21022, tc 0, ttl 255)
(label 32101, tc 0, [S], ttl 255)
0x0000: 88e5 2c00 0000 01bd 0000 0000 7d65 0001 ..,.........}e..
0x0010: 9c7b a21a f57a 50f6 92dd 23ce 383b 5ddd .{...zP...#.8;].
0x0020: ec42 f02a 38a0 1baa 458b 71ed 1bd0 12f2 .B.*8...E.q.....
0x0030: 2ef6 2e72 359a f241 ad96 5925 057f 152d ...r5..A..Y%...-
0x0040: a2cc 2b1f 6c72 45d3 dcb1 abb2 e8c2 c953 ..+.lrE........S
0x0050: d196 10dd 9325 4b91 68c4 b782 fad6 30d6 .....%K.h.....0.
0x0060: af74 f3a8 760e 3def 284d 4771 57f3 6741 .t..v.=.(MGqW.gA
0x0070: 7c22 964a e51e 53f3 f434 6e2f 435b 2369 |".J..S..4n/C[#i
0x0080: 101c 7ffb ee9e ......
21:02:50.346676 MPLS (label 21021, tc 0, ttl 254)
(label 32102, tc 0, [S], ttl 255)
0x0000: 88e5 2c00 0000 01bd 0000 0000 7d66 0001 ..,.........}f..
0x0010: 7531 db1a f7bd 4d90 d0bb a781 0345 a552 u1....M......E.R
0x0020: 8edb c762 8678 173e 6e91 cc0b 52f2 0bf5 ...b.x.>n...R...
0x0030: 6adc bf32 b9cb c728 a78d a99c 2010 dcb5 j..2...(........
0x0040: 4ec7 ceaf 0110 8e21 2e14 d996 da22 bad4 N......!....."..
0x0050: caa5 95c8 37f8 3c9d 2b68 2758 db2a 2c5c ....7.<.+h'X.*,\
0x0060: 0eab 3699 df7b 2b7e c9b9 9515 9d97 e95d ..6..{+~.......]
0x0070: d7cb 375e ffae d992 c298 c008 9be8 2aca ..7^..........*.
0x0080: 7b2c e677 1ade {,.w..
2 packets captured
2 packets received by filter
0 packets dropped by kernel
❯
❯ sudo ip netns exec clab-srexperts-pe1 tcpdump -nni eth2 -nnvvv mpls
tcpdump: listening on eth2, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), snapshot length 262144 bytes
^C21:39:52.121897 MPLS (label 21021, tc 0, ttl 254)
(label 524279, tc 0, [S], ttl 255)
0x0000: aac1 abb5 4c5e aac1 ab59 0306 0800 4500 ....L^...Y....E.
0x0010: 0054 92e9 4000 4001 c06b c0a8 3302 c0a8 .T..@[email protected]...
0x0020: 3301 0800 8227 00da 0001 f8ee 2068 0000 3....'.......h..
0x0030: 0000 9bd3 0100 0000 0000 1011 1213 1415 ................
0x0040: 1617 1819 1a1b 1c1d 1e1f 2021 2223 2425 ...........!"#$%
0x0050: 2627 2829 2a2b 2c2d 2e2f 3031 3233 3435 &'()*+,-./012345
0x0060: 3637 67
21:39:52.123862 MPLS (label 21022, tc 0, ttl 255)
(label 524277, tc 0, [S], ttl 255)
0x0000: aac1 ab59 0306 aac1 abb5 4c5e 0800 4500 ...Y......L^..E.
0x0010: 0054 aad0 0000 4001 e884 c0a8 3301 c0a8 [email protected]...
0x0020: 3302 0000 8a27 00da 0001 f8ee 2068 0000 3....'.......h..
0x0030: 0000 9bd3 0100 0000 0000 1011 1213 1415 ................
0x0040: 1617 1819 1a1b 1c1d 1e1f 2021 2223 2425 ...........!"#$%
0x0050: 2627 2829 2a2b 2c2d 2e2f 3031 3233 3435 &'()*+,-./012345
0x0060: 3637 67
2 packets captured
2 packets received by filter
0 packets dropped by kernel
❯
Note
You may also perform a remote capture directly from your laptop to your wireshark:
### Example! Replace IP and the windows/linux wireshark path
ssh nokia@<IP> "sudo ip netns exec <CONTAINER> tshark -l -i <IF1> [-i <IF2>] [-i <IFN>] -w -" | "<WIRESHARK PATH>" -k -i -
ssh nokia@<group_id>.srexperts.net "sudo ip netns exec clab-srexperts-pe1 tshark -l -i eth3 -i eth1 -i eth2 -w -" | "c:\Program Files\Wireshark\Wireshark.exe" -k -i -
1.4.3.3 ANYsec Packet Dissectors for Wireshark#
The public Wireshark installation can decode standard MACsec headers but not ANYsec (MACsec over MPLS)).
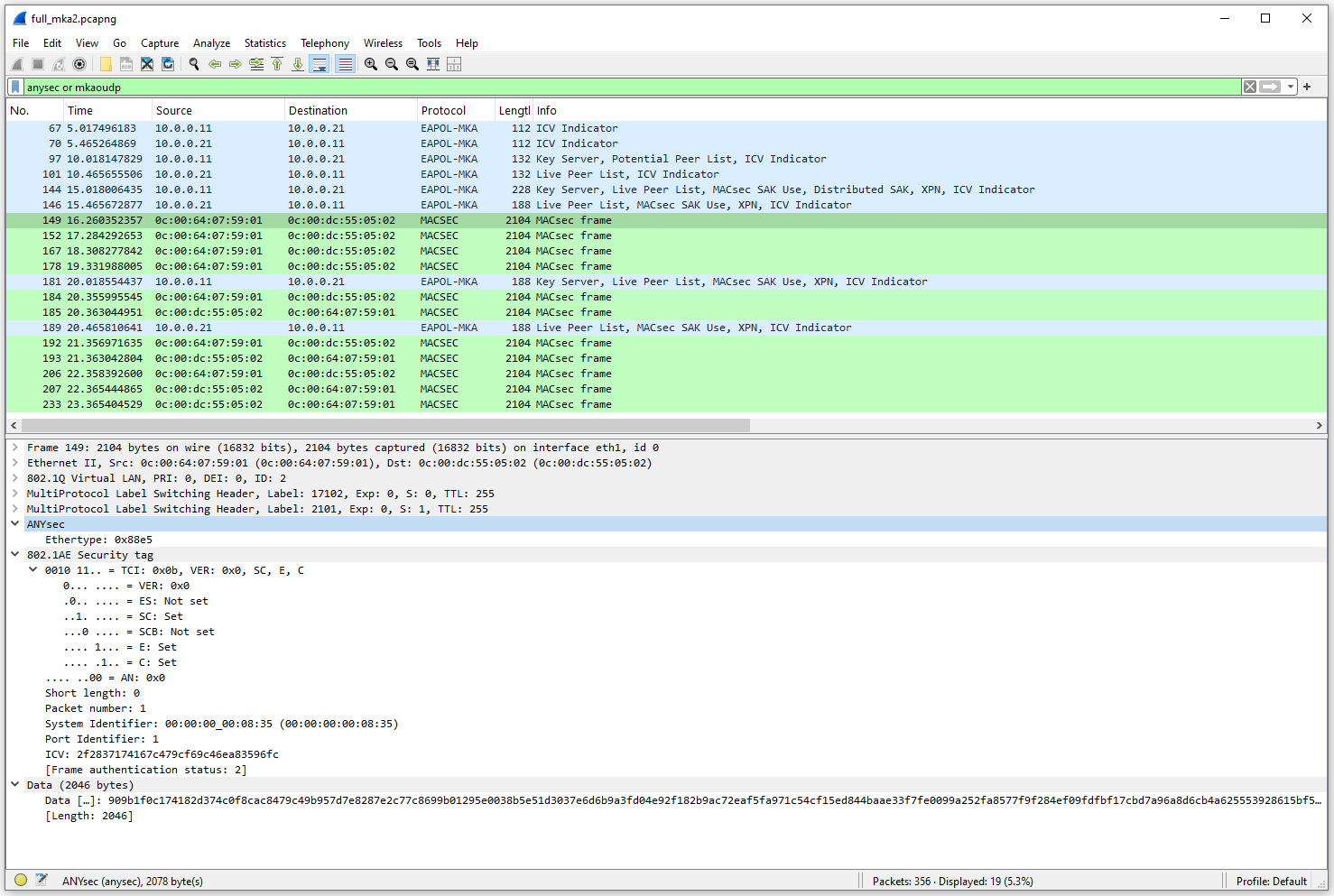
The ANYsec Packet Dissectors for Wireshark project provides Wireshark Lua plugins to decode ANYsec. If you want to inspect ANYsec in your laptop, consider installing these plugins. You'll then be able to filter by anysec or mkaoudp, and verify the header stack and the encrypted payload as show in the picture below:
Follow the instructions provided. In summary you need an up to date Wireshark version with LUA support and to copy the dissector files to your Wireshark Plugins folder.
1.4.4 Automate ANYsec services with gNMIc#
We have gone over the steps required for setting up a service between two peers that is encrypted with ANYsec. Regrettably, this involved a significant amount of manual configuration that is quite sensitive to parameters and values being aligned. Any situation where you might consider selling this to your customers via a portal where they can create, enable or disable ANYsec services at the push of a button wouldn't work if the configuration needs to be done manually.
Fortunately, we are focused on automation here. In this task we will use gNMIc calls to automate the process of creating and destroying the service.
In a real deployment, a self-service portal can be offered to your customers to align service configuration with their wishes would make these calls, though for now we will do them manually. You may use the MD-CLI explorer tool, to find the YANG paths to use.
Your new task is to build gNMIc calls that can do the following:
- Retrieve the VLL configuration present on the system in JSON format
- Create a new VLL service between two PE nodes
- Using the clients and the packet inspection techniques seen previously, make sure your calls have the expected result.
- Turn ANYsec on or off for an encryption-group between two PE nodes
- Remove the VLL service between two PE nodes
The gnmic client has been pre-installed on your group's hackathon instance and the example solution will presume this is the environment you use. You are free to install gNMIc on your local machine using the instructions available online if you are able. Use the gNMIc documentation to figure out how you can retrieve data from remote systems and provide inputs and data-structures to the tool when making changes.
Insecure mode gRPC
When using gNMIc in the following sections you will notice that the gRPC server in the model-driven SR OS nodes in the Hackathon topology is set to insecure mode. This is only suitable for a lab environment and should be changed to TLS-secured mode for any live or production environment.
1.4.4.1 Get configuration information from the system#
Before we start with the configurations let's get started with gNMIc in read-only mode. For this subtask, use only the Get RPC and use it to store the configuration from one or both PE nodes anysec-vll-1001 service in a JSON file.
Solution
This is the example solution for retrieving the service configuration using Get RPC.
gnmic -a clab-srexperts-pe1 -u admin -p $EVENT_PASSWORD --insecure get \
--path '/configure/service/epipe[service-name=anysec-vll-1001]' > pe1-anysec-vll-1001.json
gnmic -a clab-srexperts-pe2 -u admin -p $EVENT_PASSWORD --insecure get \
--path '/configure/service/epipe[service-name=anysec-vll-1001]' > pe2-anysec-vll-1001.json
1.4.4.2 Create a new VLL service between two PE nodes#
Your customer requested you to add a new VLL service. You may use the existing CA and ANYsec configurations, and you only need to configure the new VLL. Use the JSON files from previous "Get configuration information from the system" task as reference and create the configuration files for both client01 and client02 as well as the gNMIc RPC Set call. Use the following parameters for the new service:
- service-name: anysec-vll-1002
- service-id: 1002
- sap-id: 1/1/c6/1:1002
- sdp-bind-id: 1222:1002 or 1111:1002 (for PE1 and PE2 respectively)
Solution
The example solution for creating a service makes use of the Set RPC.
{
"admin-state": "enable",
"customer": "1",
"description": "Epipe using ISIS 0",
"sap": [
{
"admin-state": "enable",
"sap-id": "1/1/c6/1:1002"
}
],
"service-id": 1002,
"service-mtu": 8100,
"service-name": "anysec-vll-1002",
"spoke-sdp": [
{
"admin-state": "enable",
"sdp-bind-id": "1222:1002",
"vc-type": "ether"
}
]
}
{
"admin-state": "enable",
"customer": "1",
"description": "Epipe using ISIS 0",
"sap": [
{
"admin-state": "enable",
"sap-id": "1/1/c6/1:1002"
}
],
"service-id": 1002,
"service-mtu": 8100,
"service-name": "anysec-vll-1002",
"spoke-sdp": [
{
"admin-state": "enable",
"sdp-bind-id": "1111:1002",
"vc-type": "ether"
}
]
}
gnmic -a clab-srexperts-pe1 -u admin -p $EVENT_PASSWORD --insecure set \
--update-path '/configure/service/epipe[service-name="anysec-vll-1002"]' \
--update-file pe1-saved-data.json
gnmic -a clab-srexperts-pe2 -u admin -p $EVENT_PASSWORD --insecure set \
--update-path '/configure/service/epipe[service-name="anysec-vll-1002"]' \
--update-file pe2-saved-data.json
$ gnmic -a clab-srexperts-pe1 -u admin -p $EVENT_PASSWORD --insecure set --update-path '/configure/service/epipe[service-name="anysec-vll-1002"]' --update-file pe1-saved-data.json
{
"source": "clab-srexperts-pe1",
"timestamp": 1747000595813352651,
"time": "2025-05-12T00:56:35.813352651+03:00",
"results": [
{
"operation": "UPDATE",
"path": "configure/service/epipe[service-name=anysec-vll-1002]"
}
]
}
$
You have completed this task as you now have a gNMIc call to add service configuration to model-driven SR OS.
In a real deployment, for distinct customers you may need to deploy distinct CAs, distinct ANYsec configs and PSKs. With ANYsec you can achieve granularity per service and you can also configure slicing with traffic-engineering using e.g. Flex-Algo.
1.4.4.3 Test the new service#
Your next task is to configure the clients and test the new service with the commands below.
You may validate from the PE's CLI, using the clients and the packet inspection techniques seen previously, to make sure your calls have the expected result.
Challenge: Create gNMIC set to disable the link between the PE1 and P1 while you capture traffic and obverse the impact on the traffic.
Solution
Solution example to disable/enable the link between PE1 and P1. Note that you must disable the link on both sides.
gnmic -a clab-srexperts-pe1:57400 -u admin -p $EVENT_PASSWORD --insecure set --update-path '/configure/port[port-id=1/1/c1/1]/admin-state' --update-value disable
gnmic -a clab-srexperts-p1:57400 -u admin -p $EVENT_PASSWORD --insecure set --update-path '/configure/port[port-id=1/1/c1/1]/admin-state' --update-value disable
gnmic -a clab-srexperts-pe1:57400 -u admin -p $EVENT_PASSWORD --insecure set --update-path '/configure/port[port-id=1/1/c1/1]/admin-state' --update-value enable
gnmic -a clab-srexperts-p1:57400 -u admin -p $EVENT_PASSWORD --insecure set --update-path '/configure/port[port-id=1/1/c1/1]/admin-state' --update-value enable
Warning
Don't forget to re-enable the link again!
1.4.4.4 Toggle ANYsec with gNMIc calls#
Imagine that you need to troubleshoot a service and you need to enable or disable ANYsec encryption, or you are selling service encryption in a subscription model and you have a tool or a portal that needs to enable or disable ANYsec on-demand.
For this task, use gNMIc to access a remote system, check the state for a certain encryption-group and peer combination and turn it off if it was on initially or vice versa. This lets your portal toggle encryption quickly and easily. Use can use the configurations from previous tasks. Your call should take the following inputs:
- target node, by hostname or ip address
- credentials
- encryption-group name
- [optional] peer ip address
Solution
The example solution makes use of the Get and GetSet RPC.
gnmic -a clab-srexperts-pe1:57400 -u admin -p $EVENT_PASSWORD --insecure get --path '/configure/anysec/tunnel-encryption/encryption-group[group-name=EG_VLL-1001]/admin-state' | grep -e enable -e disable
gnmic -a clab-srexperts-pe2:57400 -u admin -p $EVENT_PASSWORD --insecure get --path '/configure/anysec/tunnel-encryption/encryption-group[group-name=EG_VLL-1001]/admin-state' | grep -e enable -e disable
gnmic -a clab-srexperts-pe1 -u admin -p $EVENT_PASSWORD --insecure getset \
--get '/configure/anysec/tunnel-encryption/encryption-group[group-name=EG_VLL-1001]/admin-state' \
--condition 'true' \
--update '.[0].updates[0].Path' \
--value '.[0].updates[0].values["configure/anysec/tunnel-encryption/encryption-group/admin-state"] | if contains("disable") then "enable" else "disable" end'
gnmic -a clab-srexperts-pe2 -u admin -p $EVENT_PASSWORD --insecure getset \
--get '/configure/anysec/tunnel-encryption/encryption-group[group-name=EG_VLL-1001]/admin-state' \
--condition 'true' \
--update '.[0].updates[0].Path' \
--value '.[0].updates[0].values["configure/anysec/tunnel-encryption/encryption-group/admin-state"] | if contains("disable") then "enable" else "disable" end'
1.4.4.5 Remove the VLL service from the PE nodes#
Lets suppose that your customer no longer needs the service and wants to remove it. With the automation portal tool a customer can always clean up their own service configurations on your PE nodes if they so wish. Use gNMIc to connect to a remote system from the CLI with the Set RPC to delete the previously created VLL anysec-vll-1002.
Solution
The example solution for deleting a service makes use of the Set RPC.
This concludes the gNMIc automation tasks.
1.4.5 Automate ANYsec services with Python#
As an optional extra task, automate the actions you have automated with gNMIc in the previous task with Python. There is no example solution for this task, though we are excited to learn what you can come up with. The subtasks here can be taken to be the same as those presented in the previous task. Use any technology or framework you prefer, though we can heartily recommend using pySROS.
1.5 Summary and Review#
Congratulations! If you have got this far you have completed this activity and achieved the following:
- You have made your network quantum safe!
- You have learned what ANYsec brings to the table in a modern networking environment
- You have configured ANYsec in model-driven FP5-based SR OS routers
- You have used ANYsec to encrypt traffic exchanged between two client sites
- You have inspected that traffic to confirm that it is indeed being encrypted
- You have automated configuration on model-driven SR OS through gRPC with
gNMIc - and you may have even automated all of this using Python and the pySROS library
This is a pretty extensive list of achievements! Well done!
If you're hungry for more have a go at another activity, or try to go further into automating the configuration of ANYsec to include things like key-rotation.