1. NDK Agent to manage static-routes based on next-hop reachability checks#
| Activity name | NDK Agent to manage static-routes based on next-hop reachability checks |
| Activity ID | 20 |
| Short Description | Nokia SRLinux NDK (NetOps Development Kit) allows users to deploy non-native apps (aka agents). These custom apps or agents run alongside native apps on SR Linux Network OS. |
| Difficulty | Intermediate |
| Tools used | NDK, Python |
| Topology Nodes | leaf11, leaf13, client02, client11, client13, pe2 |
| References | SRLinux overview NetOps Development Kit (NDK) NetOps Development Kit API Reference Apps Catalog NDK Developers Guide SR Linux applications |
In this activity you will learn about the SRLinux NDK architecture and how to deploy non-native apps (aka custom agents).
You will learn the file and folder structures and how to on-board a basic agent including the YANG data model.
Finally, you will test the agent operation, inspect the code to fix some issues, validate the proper operation and add a new feature.
The objectives of this exercise are:
- Explore the SRLinux NDK architecture and how to deploy non-native apps.
- Inspect the agents file and folder structures and the on-board process.
- Validate the agent execution, inspect the code, the logs and validate the proper operation.
- Add code for a new feature
Let's first describe the use case.
1.0.1 NDK Agent use case - static route with next-hop reachability validation#
Imagine that you have a data center with an SR Linux IP fabric and several servers hosting two services (Green and Blue) each with it's own VLAN as represented in the picture below. Each service has multiple PODs distributed across the servers but exposing a single Anycast Virtual IP (VIP) per service. There is no BGP, BFD or other dynamic protocol supported, as such, static routes are used: the Anycast IP is the destination and the sub-interface VLAN IP is the next-hop.
As long as there is a POD active for a service in a server, the VIP and the VLAN interface will remain active. The leaves will have a static-route per service with the Anycast IP as destination and the local connected servers VLAN IP as next-hop. If a server or the physical interfaces fails, the leaf detects the failure and the route becomes inactive and is no longer advertised. However, if all the PODs are moved to another server or if there's a logical failure of one service, the leaves cannot detect it and an outage occurs.
One potential solution would be to enhance the static-routes with the capability to validate the next-hop reachability, which is supported today in SROS (cpe-check feature) but not in SR Linux.
Your objective is to solve this problem using the NDK on SR Linux.
1.1 Technology explanation#
1.1.1 NetOps Development Kit (NDK)#
Nokia SR Linux provides a software development kit called NetOps Development Kit or NDK for short, that enables its users to create their own custom apps (also referred to as "agents"). These custom apps or agents run alongside native apps on SR Linux Network OS and can can deeply integrate with the rest of the SR Linux system.
Applications developed with SR Linux NDK have a set of unique characteristics which set them aside from the traditional off-box automation solutions:
- Native integration with SR Linux system, management and telemetry
- Programming language-neutral - NDK is based on gRPC, it is possible to use any programming language that supports protobuf, such as Python and Go
- Deep integration with system components
Note: Browse the Apps Catalog with a growing list of NDK apps that Nokia or 3rd parties published.
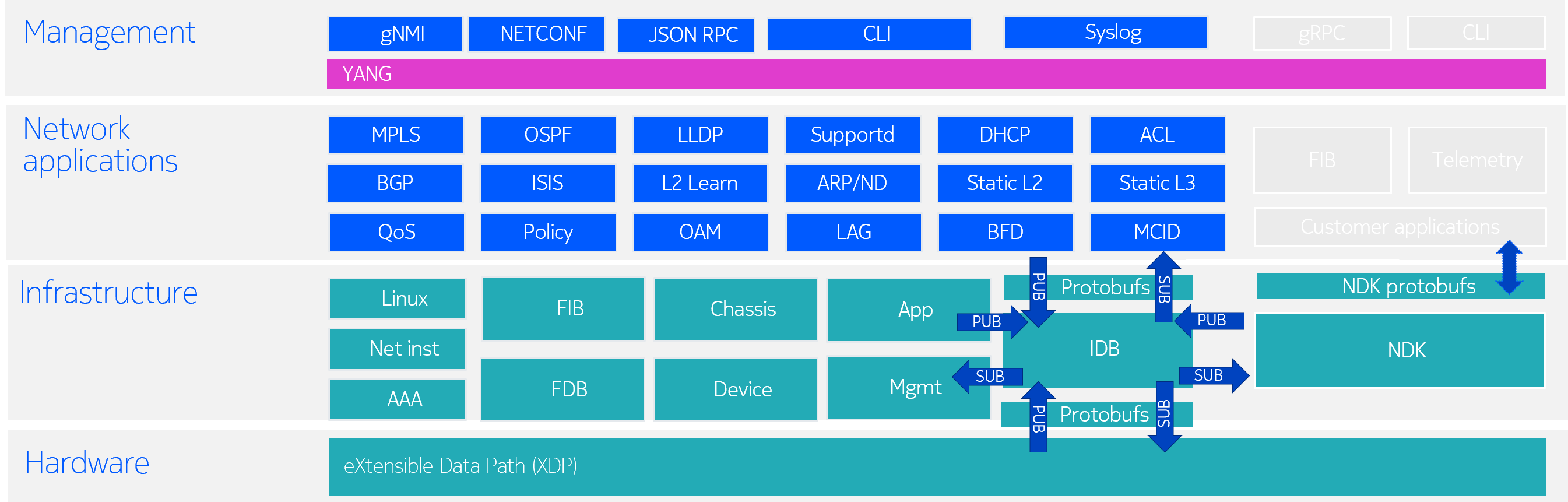
1.1.2 NDK Architecture#
The SRLinux NDK Architecture is illustrated in the Fig. 3. below. This shows how NDK gRPC service enables custom applications to interact with other SR Linux applications via Impart Database (IDB).
Custom NDK applications app-1 and app-2 interact with other SR Linux subsystems via gRPC-based NDK service that offers access to IDB. SR Linux native apps, like BGP, LLDP, and others also interface with IDB to read and write configuration and state data.
In addition to the traditional tasks of reading and writing configuration, NDK-based applications gain low-level access to the SR Linux system. For example, these apps can install FIB routes or listen to LLDP events.
Note: Developers are welcomed to dig into the NDK Developers Guide to learn all about NDK architecture and how to develop apps with this kit.
1.1.2.1 SR Linux App logs#
There are two concepts to keep in mind regarding logs and outputs that are generated by SR Linux apps:
- Standard Output/Error Redirection: All apps (native or custom)
stdout/stderroutput is redirected by default to a file (with same name as the app) under/var/log/srlinux/stdout. This is useful for debugging or displaying exceptional error conditions - such as an application crash or unhandled exception. - Operational Logging: During normal operation, apps can produce structured log messages that describe their activity, status updates, and internal events. It's up to the app developer to decide how to implement this logic and to where send the logs to. SR Linux native apps are designed to send this logs to the system
syslogdaemon, allowing users to configure syslog rules to control how and where logs are forwarded, such as to external collectors or additional local files. In addition to user-defined rules, SR Linux includes built-in (hard-coded) syslog rules that forward a copy of all native apps logs to files under/var/log/srlinux/debug/for centralized access and troubleshooting.
1.2 Access specific node/lab details#
For this activity we will use a subset of the main topology, with a pair of leaves (leaf11 and leaf13), a pair of clients (client11 and client13) configured with the Anycast IP, and a third client (client02) to test connectivity as illustrated in Fig. 4. below:
Keep in mind the following:
- An Anycast IP address is already configured at
client11andclient13. - The new agent is deployed at
leaf11andleaf13to allow the configuration of static routes to the anycast IP@ and allow next-hop validation. - A complete agent solution is deployed in
leaf13, whileleaf11agent has missing parts that will be your challenge to complete along this activity. - Probe client is deployed at
client02(to test connectivity to theclient11andclient13probe responder).
Let's now start with the activities!
1.3 Tasks#
In this section we'll provide several tasks that will allow you to learn about SR Linux native agents and the process to onboard a new agent using NDK. The agent will allow to create new static-routes with the next-hop validation capabilities. We'll need to troubleshoot the onboard process, inspect the logs, configure the static-routes, validate the full operation and add new features to the agent.
1.3.1 Inspect the native apps/agents#
First let's briefly inspect the native apps.
Login to leaf11 sr_cli and verify which applications are running. Then move to linux bash and verify the contents of the /opt/srlinux/appmgr/ folder.
Note
The sr_cli is SR Linux CLI and the linux bash is the underlying Linux shell that is running on SR Linux nodes. You can move between both using the keywords sr_cli or bash.
--{ + running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf11# show system application
+---------------------+---------+--------------------+-----------------------------------------------------------+--------------------------+
| Name | PID | State | Version | Last Change |
+=====================+=========+====================+===========================================================+==========================+
| aaa_mgr | 2095 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:33.585Z |
| acl_mgr | 2119 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:33.586Z |
| app_mgr | 1887 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:34.368Z |
| arp_nd_mgr | 2154 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:33.586Z |
| bfd_mgr | 2198 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:33.586Z |
| bgp_mgr | 6899 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:57.184Z |
| chassis_mgr | 2224 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:33.591Z |
| dev_mgr | 1951 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-04-13T11:27:07.152Z |
| dhcp_client_mgr | 2261 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:33.591Z |
| dhcp_relay_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| dhcp_server_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| dnsmasq-mgmt | 2789787 | running | 2.89 | 2025-04-14T16:34:09.562Z |
| ethcfm_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| event_mgr | 3331555 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-04-17T12:36:51.996Z |
| evpn_mgr | 2302 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:33.591Z |
| fhs_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| fib_mgr | 2336 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:33.592Z |
| grpc_server | 3379 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:38.456Z |
| idb_server | 2058 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:31.274Z |
| igmp_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| isis_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| json_rpc | 7036 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:57.507Z |
| l2_mac_learn_mgr | 2366 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:33.592Z |
| l2_mac_mgr | 2445 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:33.592Z |
| l2_proxy_arp_nd_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| l2_static_mac_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| label_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| lag_mgr | 2488 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:33.592Z |
| ldp_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| license_mgr | 2535 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:33.593Z |
| linux_mgr | 2567 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:33.593Z |
| lldp_mgr | 6946 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:57.337Z |
| log_mgr | 2614 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:33.593Z |
| macsec_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| mcid_mgr | 2656 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:33.593Z |
| mfib_mgr | 2707 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:33.593Z |
| mgmt_server | 2784688 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-04-14T16:16:50.938Z |
| mirror_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| mpls_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| net_inst_mgr | 2806 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:33.594Z |
| netconf_mgr | 2673304 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-04-14T10:58:23.092Z |
| oam_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| oc_mgmt_server | 2672247 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-04-14T10:58:12.666Z |
| ospf_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| pcc_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| pim_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| plcy_mgr | 3275 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:38.147Z |
| qos_mgr | 3289 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:38.157Z |
| radius_mgr | 2859 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:33.594Z |
| sdk_mgr | 2874 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:33.594Z |
| segrt_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| sflow_sample_mgr | 2907 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:34.383Z |
| snmp_server-mgmt | 2785392 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-04-14T16:16:58.385Z |
| sshd-mgmt | 2785340 | running | OpenSSH_9.2p1 Debian-2+deb12u3, OpenSSL 3.0.15 3 Sep 2024 | 2025-04-14T16:16:58.372Z |
| sshd-mgmt-netconf | 2785352 | running | OpenSSH_9.2p1 Debian-2+deb12u3, OpenSSL 3.0.15 3 Sep 2024 | 2025-04-14T16:16:58.379Z |
| static_route_mgr | 2087713 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-04-11T15:44:54.691Z |
| supported | 1405 | running | | 2025-03-31T15:58:30.377Z |
| te_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| twamp_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| vrrp_mgr | | waiting-for-config | | |
| vxlan_mgr | 3323 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:38.170Z |
| xdp_lc_1 | 2946 | running | v24.10.3-201-g9d0e2b9371 | 2025-03-31T15:58:34.421Z |
+---------------------+---------+--------------------+-----------------------------------------------------------+--------------------------+
--{ + running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf11#
admin@g15-leaf11:/etc/opt/srlinux$ cd /opt/srlinux/appmgr/
admin@g15-leaf11:/opt/srlinux/appmgr$ ls -al
total 296
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Feb 19 23:18 .
drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 Feb 19 23:18 ..
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Feb 19 23:18 aaa_mgr
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2452 Feb 19 22:24 cgroup_profile.json
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Feb 19 23:18 logmgr
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 3865 Feb 19 02:49 oc_yang_config.conf
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 623 Feb 19 02:49 sr_aaa_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 1853 Feb 19 02:49 sr_acl_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 702 Feb 19 02:49 sr_app_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 712 Feb 19 02:49 sr_arp_nd_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 756 Feb 19 02:49 sr_bfd_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 643 Feb 19 02:49 sr_bgp_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 2292 Feb 19 02:49 sr_chassis_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 537 Feb 19 02:49 sr_device_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 307 Feb 19 02:49 sr_dhcp_client_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 676 Feb 19 02:49 sr_dhcp_relay_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 585 Feb 19 02:49 sr_dhcp_server_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 651 Feb 19 02:49 sr_ethcfm_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 632 Feb 19 02:49 sr_event_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 781 Feb 19 02:49 sr_evpn_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 526 Feb 19 02:49 sr_fhs_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 631 Feb 19 02:49 sr_fib_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 433 Feb 19 02:49 sr_gretunnel_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 728 Feb 19 02:49 sr_grpc_server_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 387 Feb 19 02:49 sr_idb_server_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 887 Feb 19 02:49 sr_igmp_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 839 Feb 19 02:49 sr_isis_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 824 Feb 19 02:49 sr_json_rpc_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 847 Feb 19 02:49 sr_l2_mac_learn_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 1592 Feb 19 02:49 sr_l2_mac_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 654 Feb 19 02:49 sr_l2_proxy_arp_nd_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 510 Feb 19 02:49 sr_l2_static_mac_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 517 Feb 19 02:49 sr_label_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 506 Feb 19 02:49 sr_lag_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 534 Feb 19 02:49 sr_ldp_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 541 Feb 19 02:49 sr_license_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 3464 Feb 19 02:49 sr_linux_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 598 Feb 19 02:49 sr_lldp_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 431 Feb 19 02:49 sr_log_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 565 Feb 19 02:49 sr_macsec_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 975 Feb 19 02:49 sr_mcid_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 1057 Feb 19 02:49 sr_mfib_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 945 Feb 19 02:49 sr_mgmt_server_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 639 Feb 19 02:49 sr_mirror_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 497 Feb 19 02:49 sr_mpls_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 620 Feb 19 02:49 sr_mplsoam_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 992 Feb 19 02:49 sr_net_inst_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 723 Feb 19 02:49 sr_netconf_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 532 Feb 19 02:49 sr_oam_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 635 Feb 19 02:49 sr_oc_mgmt_server_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 539 Feb 19 02:49 sr_ospf_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 494 Feb 19 02:49 sr_pcc_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 990 Feb 19 02:49 sr_pim_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 380 Feb 19 02:49 sr_pinger_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 902 Feb 19 02:49 sr_plcy_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 653 Feb 19 02:49 sr_pw_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 830 Feb 19 02:49 sr_qos_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 198 Feb 19 02:49 sr_radius_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 326 Feb 19 02:49 sr_sdk_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 456 Feb 19 02:49 sr_segrt_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 361 Feb 19 02:49 sr_sflow_sample_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 603 Feb 19 02:49 sr_static_route_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 375 Feb 19 02:49 sr_supportd_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 954 Feb 19 02:49 sr_te_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 817 Feb 19 02:49 sr_tepolicy_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 1219 Feb 19 02:49 sr_time_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 838 Feb 19 02:49 sr_timing_stack_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 751 Feb 19 02:49 sr_twamp_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 974 Feb 19 02:49 sr_vrrp_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 930 Feb 19 02:49 sr_vxlan_mgr_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 405 Feb 19 02:49 sr_xdp_cpm_config.yml
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root root 542 Feb 19 02:49 sr_xdp_lc_config.yml
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1411 Feb 19 22:24 upgradability.json
admin@g15-leaf11:/opt/srlinux/appmgr$
The previous outputs shows the native apps and their definition files.
1.3.2 Inspect the custom agent#
Keep the ssh session to leaf11 open and create a new one to leaf13.
Verify that a custom app srl_basic_agent is running. Compare the output against the one from leaf11. Then move to linux bash and verify the contents of the /etc/opt/srlinux/appmgr/ folder.
--{ running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf13# show system application srl_basic_agent
+-----------------+---------+---------+---------+--------------------------+
| Name | PID | State | Version | Last Change |
+=================+=========+=========+=========+==========================+
| srl_basic_agent | 2717566 | running | v1.0 | 2025-04-22T12:13:53.720Z |
+-----------------+---------+---------+---------+--------------------------+
--{ running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf13#
admin@g15-leaf13:/etc/opt/srlinux/appmgr$ ls -al -R
.:
total 24
drwxrwxrwx+ 3 srlinux srlinux 4096 Apr 23 17:35 .
drwxrwxrwx+ 14 srlinux srlinux 4096 Apr 22 12:04 ..
drwxrwxrwx 3 admin ntwkuser 4096 Apr 22 12:04 srl_basic_agent
-rw-rw-r--+ 1 admin ntwkuser 887 Apr 22 11:53 srl_basic_agent.yml
./srl_basic_agent:
total 48
drwxrwxrwx 3 admin ntwkuser 4096 Apr 22 12:04 .
drwxrwxrwx+ 3 srlinux srlinux 4096 Apr 23 17:35 ..
-rwxrwxrwx 1 admin ntwkuser 21718 Apr 22 12:04 srl_basic_agent.py
-rwxrwxrwx 1 admin ntwkuser 786 Apr 22 11:59 srl_basic_agent.sh
-rwxrwxrwx 1 admin ntwkuser 24 Apr 22 12:02 srl_basic_agent_version.sh
drwxrwxrwx 2 admin ntwkuser 4096 Apr 22 12:01 yang
./srl_basic_agent/yang:
total 12
drwxrwxrwx 2 admin ntwkuser 4096 Apr 22 12:01 .
drwxrwxrwx 3 admin ntwkuser 4096 Apr 22 12:04 ..
-rwxrwxrwx 1 admin ntwkuser 2467 Apr 22 12:01 srl_basic_agent.yang
admin@g15-leaf13:/etc/opt/srlinux/appmgr$
The previous outputs shows the custom app/agent and its configuration files.
Is the srl_basic_agent agent running on both leafs?
Solution
The agent is running at leaf13 but not at leaf11. This is intended, because we introduce some issues that you need to solve in the following tasks!
1.3.3 Onboard agent troubleshoot#
At boot up, the SR Linux App Manager (app_mgr) looks for third-party apps .yml files in the /etc/opt/srlinux/appmgr/ directory and loads them automatically.
The onboarding of an NDK agent onto the SR Linux consists in copying the agent and its files over to the SR Linux filesystem and placing them in the directories. The agent installation procedure can be carried out in different ways: manual, automated or with deb packages.
The following agent files have been onboarded to both leaf11 and leaf13 for you already (using the CLAB bind feature):
| Component | Filesystem location |
|---|---|
| Definition file | /etc/opt/srlinux/appmgr/srl_basic_agent.yml |
| Executable file | /etc/opt/srlinux/appmgr/srl_basic_agent/srl_basic_agent.sh |
| YANG modules | /etc/opt/srlinux/appmgr/srl_basic_agent/yang/srl_basic_agent.yang |
| Agent version | /etc/opt/srlinux/appmgr/srl_basic_agent/srl_basic_agent_version.sh |
| Agent Python code | /etc/opt/srlinux/appmgr/srl_basic_agent/srl_basic_agent.py |
Warning
The agent version differs between leaf13 and leaf11.
A complete working agent solution for this activity is deployed in leaf13, while leaf11 agent has missing parts that will be your challenge to complete along this activity.
Note
The agent files are located in your group's hackaton VM instance at activities/nos/srlinux/20-SRLinux-basic-agent. The leaf11_agent folder is binded to to the leaf11 /etc/opt/srlinux/appmgr/, so you can edit the files directly on the Hackaton VM host using Visual Studio code or any other editor.
From the previous task we saw that the agent is running on leaf13 but not on leaf11.
Your task is to figure out why the agent is not running in leaf11 and fix the issue.
Stop and take time to think here
- What is the first kind of file that system looks for to discover and load apps?
- Is it possible to check details about the app status, in addition to what is displayed by
show system application? For example, how can you confirm that the parameters defined in.ymlfile were loaded as expected. - What logs can be checked to help investigate the reason about why an app is not entering
runningstate?
Hint 1
- Check out Agent Components to know what key fields need to be filled in the definition
.ymlfile. - You may also check examples of other custom apps in the Apps Catalog
Hint 2
You need to inspect agent .yang file, to know what needs to be filled in yang-modules: section of the definition .yml file.
After modifying the app .yml file, how to signal the system to rediscover and process app .yml changes? This documentation piece can help you Agent Installation & Operations - Loading the agent
Hint 3
Search for a path in the state datastore that represent detailed status about loaded apps.
Warning
During your attempts to load the app, if you introduce errors in the .yml file that conflicts with native SR Linux apps, the system might get into an unexpected state where you observe symptoms such as:
- missing information on
runningorstatedatastore - lose ssh access to the leaf
To recover, perform a restart of the mgmt_server native app with tools system app-management application mgmt_server restart. Take this into account for the remainder tasks of the activity.
Solution
The /etc/opt/srlinux/appmgr/srl_basic_agent.yml is empty at leaf11 and that's why the app is not loading.
So you need to update your VM file at:
activities/nos/srlinux/20-SRLinux-basic-agent/leaf11_agent/srl_basic_agent.yml.
You may also update leaf11's directly, e.g., with vi:
/etc/opt/srlinux/appmgr/srl_basic_agent.yml
Note: You can copy/paste code directly to
vi, howhever, to keep your indentation you need to enable paste mode (Esc +:set paste) then move to insertation mode and paste your code.
Once you fix the file you need to reload the app_mgr and verify that the srl_basic_agent is running. You may inspect the app status, version and state info with the following commands:
--{ running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf11# show system application srl_basic_agent
+-----------------+---------+---------+---------+--------------------------+
| Name | PID | State | Version | Last Change |
+=================+=========+=========+=========+==========================+
| srl_basic_agent | 2177265 | running | v0.5 | 2025-04-24T10:48:49.851Z |
+-----------------+---------+---------+---------+--------------------------+
--{ running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf11#
--{ running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf11# info from state system app-management application srl_basic_agent
system {
app-management {
application srl_basic_agent {
pid 120406
state running
last-change "2025-04-27T17:19:33.203Z (37 minutes ago)"
last-start-type cold
author "Nokia SReXperts"
failure-threshold 3
failure-window 300
failure-action wait=10
path /etc/opt/srlinux/appmgr/srl_basic_agent/
launch-command "sudo /etc/opt/srlinux/appmgr/srl_basic_agent/srl_basic_agent.sh"
search-command "/bin/bash /etc/opt/srlinux/appmgr/srl_basic_agent/srl_basic_agent.sh"
version v0.5
oom-score-adj 0
supported-restart-types [
cold
]
restricted-operations [
quit
]
statistics {
restart-count 52
}
yang {
modules [
srl_basic_agent
]
source-directories [
/opt/srl_basic_agent/yang
/opt/srlinux/models/iana
/opt/srlinux/models/ietf
/opt/srlinux/models/srl_nokia/models
]
}
}
}
}
--{ running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf11#
1.3.4 Inspect the Agent logs#
Open 2 new tabs to the leaf11 bash and inspect the 2 agent logs files created under /var/log/srlinux/stdout:
- srl_basic_agent.log - file created by the app_mgr to save
stdout/stderroutput of the app. You should see no errors. - srl_basic_agent_python.log - custom log file created by
srl_basic_agent.py. You should see keepalives
1.3.5 Configure the new static routes#
Now that the agent is running on both leafs, its time to put it into action! The objective is to ensure reachability between the probe client and the probe responders' Anycast IP address. To accomplish this, you will use the custom agent to configure the static routes.
The next-hop IP address reachability shall be periodically tested, such that when the next-hop becomes unreachable, respective static-route is automatically deactivated by the agent until reachability is restored.
Your next task is to configure the new static routes in leaf11 and leaf13 under ipvrf201 as shown in the diagram below:
Question
The agent should expose a new configuration knob in candidate datastore that allows to manage the static routes. Can you find it out?
Tip
You should see that under any ip-vrf instance there's a new option available: static-routes-ndk
Solution
1.3.6 Verify the agent normal operation#
Now that you have configured both leaf11 and leaf13, you can verify the agent operation.
The agent is supposed to consume configuration and populate state under the YANG path /network-instance <name> static-routes-ndk.
--{ + running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf13# info from state / network-instance ipvrf201 static-routes-ndk
network-instance ipvrf201 {
static-routes-ndk {
route 192.168.31.1/32 {
admin-state enable
next-hop 192.168.30.13
cpe-check {
admin-state enable
is-alive true
probe-statistics {
successful 17998
failed 0
}
}
}
}
}
--{ + running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf11# show network-instance ipvrf201 route-table ipv4-unicast prefix 192.168.31.1/32
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
IPv4 unicast route table of network instance ipvrf201
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+---------------------------+-------+------------+----------------------+----------+----------+---------+------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+----------------------+
| Prefix | ID | Route Type | Route Owner | Active | Origin | Metric | Pref | Next-hop (Type) | Next-hop | Backup Next-hop | Backup Next-hop |
| | | | | | Network | | | | Interface | (Type) | Interface |
| | | | | | Instance | | | | | | |
+===========================+=======+============+======================+==========+==========+=========+============+=================+=================+=================+======================+
| 192.168.31.1/32 | 0 | bgp-evpn | bgp_evpn_mgr | False | ipvrf201 | 0 | 170 | 10.46.15.35/32 | | | |
| | | | | | | | | (indirect/vxlan | | | |
| | | | | | | | | ) | | | |
| 192.168.31.1/32 | 10 | ndk1 | srl_basic_agent | True | ipvrf201 | 10 | 10 | 192.168.30.0/24 | irb0.101 | | |
| | | | | | | | | (indirect/local | | | |
| | | | | | | | | ) | | | |
+---------------------------+-------+------------+----------------------+----------+----------+---------+------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+----------------------+
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--{ + running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf11#
--{ + running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf11# ping network-instance ipvrf201 192.168.31.1 -c 2
Using network instance ipvrf201
PING 192.168.31.1 (192.168.31.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.31.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.84 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.31.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=2.21 ms
--- 192.168.31.1 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1001ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 1.842/2.027/2.212/0.185 ms
--{ + running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf11#
Note from the output that there are 2 routes to 192.168.31.1, the static-route installed by the agent identified as ndk1, and the route received from the other leaf through bgp-evpn. Only the local route is active, being the bgp-evpn in standby.
Note that there is also no state populated in leaf11. This is one of the missing parts that you will be challenged to complete in a later task.
1.3.7 Verify the agent operation under failure#
To properly test the end-to-end the agent operation including failure scenarios, a probe client and probe responders will be used according to the table below:
| Component | Filesystem location | Nodes |
|---|---|---|
| probe client | /probe.sh | client02 |
| probe responder | /probe-responder.sh | client11 and client13 |
The probe-responderis already installed and running at client11 and client13. On client02 start the probe requests and verify that you're getting answers from both client11 and client13 (rate of 2 requests per second).
/probe.sh 192.168.31.1
Probing 192.168.31.1:9999 using TCP...
Tue Apr 29 16:58:01 UTC 2025 - Response from client13
Tue Apr 29 16:58:01 UTC 2025 - Response from client11
Tue Apr 29 16:58:02 UTC 2025 - Response from client13
Tue Apr 29 16:58:02 UTC 2025 - Response from client13
Tue Apr 29 16:58:03 UTC 2025 - Response from client11
Tue Apr 29 16:58:03 UTC 2025 - Response from client11
Tue Apr 29 16:58:04 UTC 2025 - Response from client11
^C
Recall that the destination is an anycast address and sessions are load balanced across available targets. If you don't get the expected result, have a look to the troobleshoot tips below, otherwise skip it and proceed the exercise.
Troubleshoot the probe operation
If you face any issues with the probes follow these steps:
- Ensure the probe client and responders files exists at the hosts as listed in the table above.
- Verify the file execution permissions and the script code.
- verify that the responder is running on both
client11andclient13with:ps -ef | grep probe - If the probes are not running start them with:
setsid /probe-responder.sh - Verify ip connectivity, arp, mac and routing tables.
#!/bin/bash
#usage: ./probe.sh <target-ip> [interval in seconds]
# Activity #20 SR Linux basic agent - Probe client
TARGET="$1"
PORT="9999"
INTERVAL="${2:-0.5}" # Default interval between probes (in seconds)
TIMEOUT=1
echo "Probing $TARGET:$PORT using TCP..."
while true; do
RESPONSE=$(echo "ping" | socat -T "$TIMEOUT" - TCP:"$TARGET":$PORT,connect-timeout="$TIMEOUT")
if [ -n "$RESPONSE" ]; then
echo "$(date) - Response from $RESPONSE"
sleep "$INTERVAL"
else
echo "$(date) - No response or refused connection"
sleep $INTERVAL
fi
done
#!/bin/bash
# start the probe responder: setsid /probe-responder.sh
# Activity #20 SR Linux basic agent - Probe server
#redirect stderr and stdout to a log file
exec >/tmp/"$0".log 2>&1
PORT=9999
HOSTNAME=$(hostname)
echo "Responder listening on TCP port $PORT..."
socat TCP-LISTEN:$PORT,reuseaddr,fork SYSTEM:"echo $HOSTNAME"
Now lets introduce a failure to view the agent in action.
- Open a session to
client11andclient13to verify the routing tables before and after the failure. - Keep an open session for
client02with the probe client running. - Log in to
client11and shutdown the interfaceeth1.101with the commands below.
Tue Apr 29 19:03:53 UTC 2025 - Response from client13
Tue Apr 29 19:03:53 UTC 2025 - Response from client13
Tue Apr 29 19:03:54 UTC 2025 - Response from client11
Tue Apr 29 19:03:54 UTC 2025 - Response from client11
Tue Apr 29 19:03:55 UTC 2025 - Response from client13
2025/04/29 19:03:56 socat[15650] E connecting to AF=2 192.168.31.1:9999: Operation timed out
Tue Apr 29 19:03:56 UTC 2025 - No response or refused connection
Tue Apr 29 19:03:57 UTC 2025 - Response from client13
Tue Apr 29 19:03:57 UTC 2025 - Response from client13
Tue Apr 29 19:03:58 UTC 2025 - Response from client13
Tue Apr 29 19:03:58 UTC 2025 - Response from client13
--{ + running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf11# show network-instance ipvrf201 route-table ipv4-unicast prefix 192.168.31.1/32
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
IPv4 unicast route table of network instance ipvrf201
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+---------------------------+-------+------------+----------------------+----------+----------+---------+------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+----------------------+
| Prefix | ID | Route Type | Route Owner | Active | Origin | Metric | Pref | Next-hop (Type) | Next-hop | Backup Next-hop | Backup Next-hop |
| | | | | | Network | | | | Interface | (Type) | Interface |
| | | | | | Instance | | | | | | |
+===========================+=======+============+======================+==========+==========+=========+============+=================+=================+=================+======================+
| 192.168.31.1/32 | 0 | bgp-evpn | bgp_evpn_mgr | False | ipvrf201 | 0 | 170 | 10.46.15.35/32 | | | |
| | | | | | | | | (indirect/vxlan | | | |
| | | | | | | | | ) | | | |
| 192.168.31.1/32 | 10 | ndk1 | srl_basic_agent | True | ipvrf201 | 10 | 10 | 192.168.30.0/24 | irb0.101 | | |
| | | | | | | | | (indirect/local | | | |
| | | | | | | | | ) | | | |
+---------------------------+-------+------------+----------------------+----------+----------+---------+------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+----------------------+
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--{ + running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf11# show network-instance ipvrf201 route-table ipv4-unicast prefix 192.168.31.1/32
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
IPv4 unicast route table of network instance ipvrf201
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+---------------------------+-------+------------+----------------------+----------+----------+---------+------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+----------------------+
| Prefix | ID | Route Type | Route Owner | Active | Origin | Metric | Pref | Next-hop (Type) | Next-hop | Backup Next-hop | Backup Next-hop |
| | | | | | Network | | | | Interface | (Type) | Interface |
| | | | | | Instance | | | | | | |
+===========================+=======+============+======================+==========+==========+=========+============+=================+=================+=================+======================+
| 192.168.31.1/32 | 0 | bgp-evpn | bgp_evpn_mgr | True | ipvrf201 | 0 | 170 | 10.46.15.35/32 | | | |
| | | | | | | | | (indirect/vxlan | | | |
| | | | | | | | | ) | | | |
+---------------------------+-------+------------+----------------------+----------+----------+---------+------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+----------------------+
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--{ + running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf11#
Current mode: + running
--{ + running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf13# show network-instance ipvrf201 route-table ipv4-unicast prefix 192.168.31.1/32
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
IPv4 unicast route table of network instance ipvrf201
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+---------------------------+-------+------------+----------------------+----------+----------+---------+------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+----------------------+
| Prefix | ID | Route Type | Route Owner | Active | Origin | Metric | Pref | Next-hop (Type) | Next-hop | Backup Next-hop | Backup Next-hop |
| | | | | | Network | | | | Interface | (Type) | Interface |
| | | | | | Instance | | | | | | |
+===========================+=======+============+======================+==========+==========+=========+============+=================+=================+=================+======================+
| 192.168.31.1/32 | 0 | bgp-evpn | bgp_evpn_mgr | False | ipvrf201 | 0 | 170 | 10.46.15.33/32 | | | |
| | | | | | | | | (indirect/vxlan | | | |
| | | | | | | | | ) | | | |
| 192.168.31.1/32 | 10 | ndk1 | srl_basic_agent | True | ipvrf201 | 10 | 10 | 192.168.30.0/24 | irb0.101 | | |
| | | | | | | | | (indirect/local | | | |
| | | | | | | | | ) | | | |
+---------------------------+-------+------------+----------------------+----------+----------+---------+------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+----------------------+
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--{ + running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf13#
--{ + running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf13# show network-instance ipvrf201 route-table ipv4-unicast prefix 192.168.31.1/32
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
IPv4 unicast route table of network instance ipvrf201
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+---------------------------+-------+------------+----------------------+----------+----------+---------+------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+----------------------+
| Prefix | ID | Route Type | Route Owner | Active | Origin | Metric | Pref | Next-hop (Type) | Next-hop | Backup Next-hop | Backup Next-hop |
| | | | | | Network | | | | Interface | (Type) | Interface |
| | | | | | Instance | | | | | | |
+===========================+=======+============+======================+==========+==========+=========+============+=================+=================+=================+======================+
| 192.168.31.1/32 | 10 | ndk1 | srl_basic_agent | True | ipvrf201 | 10 | 10 | 192.168.30.0/24 | irb0.101 | | |
| | | | | | | | | (indirect/local | | | |
| | | | | | | | | ) | | | |
+---------------------------+-------+------------+----------------------+----------+----------+---------+------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+----------------------+
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--{ + running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf13#
[/]
A:admin@g15-pe2# show router "300" route-table 192.168.31.1
===============================================================================
Route Table (Service: 300)
===============================================================================
Dest Prefix[Flags] Type Proto Age Pref
Next Hop[Interface Name] Metric
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
192.168.31.1/32 Remote EVPN-IFL 00h04m48s 170
10.46.15.33 (tunneled:VXLAN:201) 0
192.168.31.1/32 Remote EVPN-IFL 00h04m48s 170
10.46.15.35 (tunneled:VXLAN:201) 0
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
No. of Routes: 2
Flags: n = Number of times nexthop is repeated
B = BGP backup route available
L = LFA nexthop available
S = Sticky ECMP requested
===============================================================================
[/]
A:admin@g15-pe2# show router "300" route-table 192.168.31.1
===============================================================================
Route Table (Service: 300)
===============================================================================
Dest Prefix[Flags] Type Proto Age Pref
Next Hop[Interface Name] Metric
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
192.168.31.1/32 Remote EVPN-IFL 00h58m22s 170
10.46.15.35 (tunneled:VXLAN:201) 0
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
No. of Routes: 1
Flags: n = Number of times nexthop is repeated
B = BGP backup route available
L = LFA nexthop available
S = Sticky ECMP requested
===============================================================================
[/]
A:admin@g15-pe2#
Note that convergence is very fast and immediately after the failure all the probes requests are responded by leaf13 only. The leaf11 removes its local static-route and installs the bgp-evpn route received from leaf13. leaf13 has only its own local route and PE2 has only one bgp-evpn from leaf13.
Warning
Don't forget to bring up the interface again!
1.3.8 Make leaf11 agent populate the state datastore#
As you have observed in the "Verify the agent normal operation" task, the agent in leaf11 is not populating the state datastore.
Can you find out why and fix the issue?
Hint 1
Analyze the srl_basic_agent.py code in leaf11. Is there any method or function responsible to update the state datastore?
Hint 2
The function update_state_datastore needs to be completed.
Hint 3
- Check the NDK documentation to find what is the appropriate gRPC call to update the
statedatastore - Check the Python NDK bindings to find the respective Python function for the gRPC call.
- Check examples from similar code in this agent, or from the Apps Catalog
Note
You need to restart the agent for the python code changes to take effect. What command you can use for this?
Check the Agent Install and Operations.
Once you complete this task the state will be populated as shown below:
Solution
def update_state_datastore(js_path, js_data):
# create gRPC client stub for the Telemetry Service
telemetry_stub = telemetry_service_pb2_grpc.SdkMgrTelemetryServiceStub(channel)
# Build an telemetry update service request
telemetry_update_request = telemetry_service_pb2.TelemetryUpdateRequest()
# Add the YANG Path and Attribute/Value pair to the request
telemetry_info = telemetry_update_request.state.add()
telemetry_info.key.js_path = js_path
telemetry_info.data.json_content = js_data
# Log the request
logging.info(f"Telemetry_Update_Request ::\{telemetry_update_request}")
# Call the telemetry RPC
telemetry_response = telemetry_stub.TelemetryAddOrUpdate(
request=telemetry_update_request,
metadata=metadata)
return telemetry_response
1.3.9 Add a feature to store basic statistics about next-hop-check probes#
We would like really to challenge you for your final task.
Modify leaf11's agent so that users are able to track (via the state datastore) the total number of successful and failed next-hop-check icmp probes (per static-route).
Here's an example of what's expected:
--{ + candidate shared default }--[ network-instance ipvrf201 static-routes-ndk route
192.168.31.1/32 ]--
A:g15-leaf11# info from state
admin-state enable
next-hop 192.168.30.11
cpe-check {
admin-state enable
is-alive false
probe-statistics {
successful 73
failed 539
}
}
Tip
You first need to edit the srl_basic_agent.yang to include a new container probe-statistics under the container cpe-check including leaves uint64 for each counter.
Then you need to edit the srl_basic_agent.py and:
- add new variables for the counters;
- update the
update_telemetrymethod; - update the
update_alivenessmethod to update the counters and telemetry.
Finally, reload the app_mgr and verify that the srl_basic_agent is running:
Solution
The outputs bellow shown the required code highlighted in blue.
--{ running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf11# show system application srl_basic_agent
+-----------------+---------+---------+---------+--------------------------+
| Name | PID | State | Version | Last Change |
+=================+=========+=========+=========+==========================+
| srl_basic_agent | 2177265 | running | v1.0 | 2025-04-24T10:48:49.851Z |
+-----------------+---------+---------+---------+--------------------------+
--{ running }--[ ]--
A:g15-leaf11#
And this concludes the activities we've prepared for you.
These activities demonstrated how SR Linux agents work, how you can use NDK to create your own agents and the flexibility you have with SR Linux custom agents.
1.4 Summary and review#
Congratulations! If you have got this far you have completed this activity and achieved the following:
- Explored the NDK architecture.
- Understood the native and custom agents/apps file and folder structure and how to onboard new agents.
- Verified agent operations, their logs and their state info.
- Configured the new
SR_CLI static-routeprovided by the agent, and tested it under normal and network failure situations. - Updated the custom agent YANG and Python scripts to include telemetry stats.
You may explore the references for more information about developing Python or Go SR Linux agents.
We hope you find this information useful and that you liked the activity.
Now we invite you to try another amazing Hackathon activity.